
Apart from leading countries South Korea & Japan, most South Asian countries including Malaysia are lagging behind.
...Malaysia saw a sharp decrease in the average download speed (both mobile and fixed broadband) from the March 16 till the March 22.
The significance of that particular time interval (March 16-22) is that the MCO was imposed in Malaysia from the March 18.
This could mean that the decrease in average speeds in Malaysia could be down to an increased strain being placed upon network operators in the country.
Conversely, the average download speed over fixed broadband in China and Japan has improved, with both countries also hit by effects of the pandemic.
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites are miniaturized, orbiting versions that operate between 500 and 2000 kilometers above Earth's surface and weigh under 500kg
Due to its low orbit, latency is significantly reduced as the satellite is better positioned to quickly receive and transmit data. Generally, fiber's latency speed is slightly faster than that of cable internet, which is usually around 30ms. However, recently satellite tech is advancing; for instance, US satellite internet service Starlink, is expected to launch with a latency below 20 ms and possibly lower in the future.
LEO satellites continuously hand off communication signals and traffic across a constellation of satellites. This ensures seamless, wide-scale coverage over a pre-defined geographical area. Not only is the inter-satellite solution providing better latency performance, it also guarantees a much better level of security by avoiding ground stations.
LEO mainly use Ka band and some V band as well. These frequencies enable higher data rates, smaller antennas, narrower beams, greater security and less vulnerable to weather and rain fade. In addition to better use of spectrum, the advancement of active antennas and processing have raised throughput per individual satellite and increasing constellation capacity.
As there will be large numbers of satellites, LEO are better compatible with antennas Electronically Scanned Apertures (ESAs), also called Electronically Steerable Antennas, which can shift beams and track and access large numbers of satellites without physical movement as opposed to the traditional parabolic-dish antennas.
By leveraging the advancement of analytics, combined with improved computing power and artificial-intelligence (AI) algorithms, response times and operating costs can be reduced.
Likewise, the throughput increase by Intersatellite Link (ISL) also reduces backhaul costs, improve satellite control and network latency.
Combining these elements would promote the autonomous and semiautonomous control and management of spacecraft, thereby reducing staffing requirements.
Low Latency compared to fiber internet
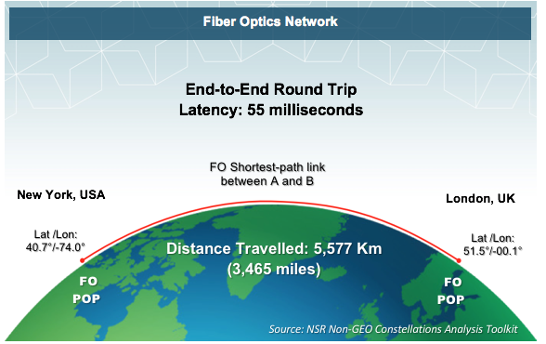
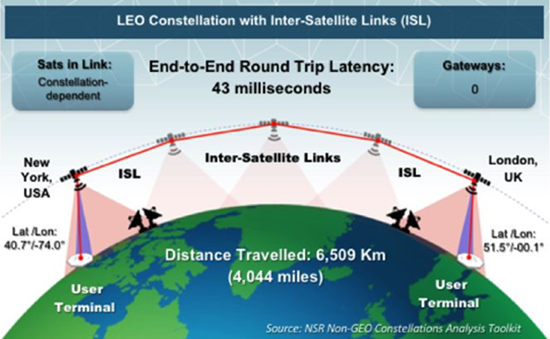
From NYC, USA to London, UK; the latency is much lower compared to traditional fiber (approximately 55 milliseconds) given that they are both cities are on the opposite sides of the world.
Currently, a round trip satellite latency is approximately 43 milliseconds.


Low Cost for Deployment of 5G in Southeast Asia
Increase in Technology and Economic Growth
Better Manageability of Network Infrastructure
Faster Deployment of Network Availability
Reduces Unnecessary Costs Expenditure
Creates an epicenter for a Joint Economic Development
Emerge as a "Unicorn" in the rise of Telecommunication Industry
Expansion of network across the country as well as neighbouring countries
Improves Quality of Experience (QoE) in high capacity applications
Provides as backup network in the event of an interference in any man-made 5G infrastructure
Provides better coverage and broadcast capabilities to support Internet of Things (IoT)
The next generation connectivity via satellite will help to develop & boost a totally new generation of start-ups ecosystem in Borneo & surrounding region
With the new generation of connectivity via low orbit satellite, downstream business such as E-commerce transactions, Business Application Development, Network Security, Cloud infrastructure and Data Centre will take off via application related to space tech and next generation R&D
Regional economy growth leading to further investment in this region and fostering good working relations with neighbouring countries in jointly managed promotional activities